Thermograms analyze the blood flow and temperature differences in the breasts. Thermography is a superficial screening procedure which is an effective tool for women to monitor small changes in the blood flow of their breasts.
When the breast is cooled in a temperature controlled room, blood vessels of normal tissue may respond by constricting to conserve heat while tumor tissue and its blood vessels may remain hot. Each individual woman has a unique "thermal signature" that remains constant over years unless there is a change. Thus, over time, it is possible to differentiate between cancers and benign conditions. It is important to have a baseline early on in a woman's life. For this reason, women should have breast thermography performed as early as age 25.
ABNORMAL THERMOGRAM
Blood vessels can form specific patterns that may signal an abnormality. To view these patterns clearly, it is vital for images to be in grey. Notice in this example vascular pattern (in grey) was noted as "highly unusual" on first study, before color images showed abnormality. Two years later, color images finally detailed abnormality that had been seen with grey one year previous.
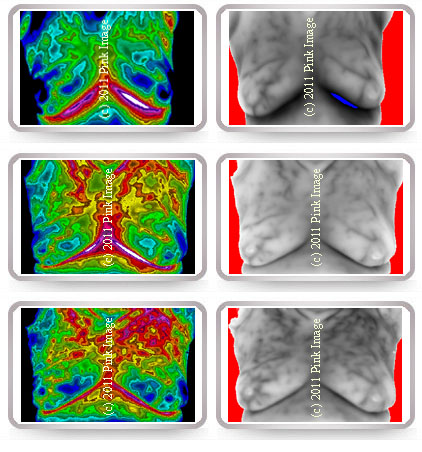
Progression of thermal vascular pattern over time. The first set is the baseline, in which the greyscale image detailed an unusual hypervascular pattern (Bilateral TH-2). In the second set, the left breast was upgraded to Equivocal (Equivocal, TH-3). After the third set was taken, left breast was again upgraded to Abnormal (Abnormal, TH-4). Ultrasound and MRI were both reported positive, confirming previous thermographic findings.
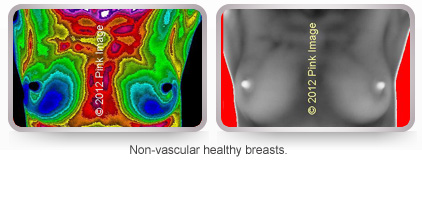
Healthy, non-vascular breasts images shown in color and grayscale. Note uniformity of colors indicating no abnormal vascular structure.
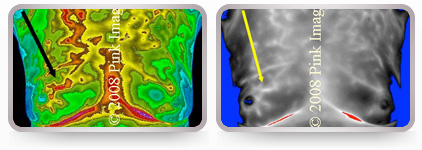
Suspected malignancy in right breast. Note increased temperature in vascular structure above right nipple.
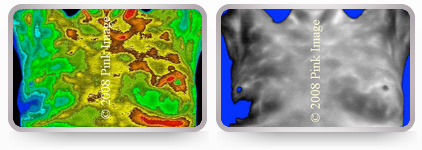
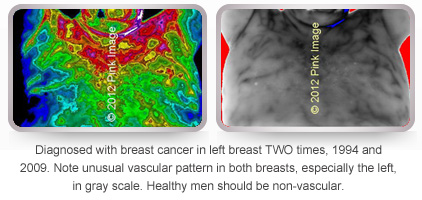
Breast cancer in left breast. Warmer tones indicate increased temperature in left breast. Note vascularity in grey image. Cancer was later confirmed by biopsy.
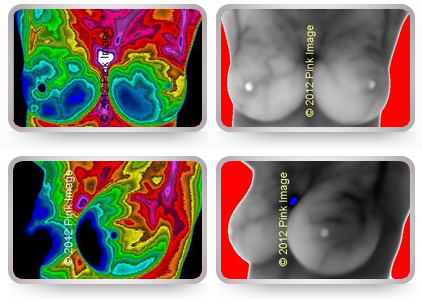
Breast cancer of left breast in 36 year old. Red and yellow tones indicates area of cancer. Note vascularity in gray image.
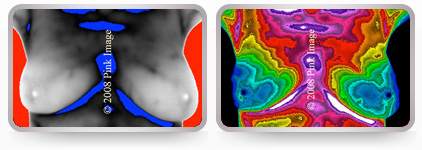
HEALTHY VS AT RISK
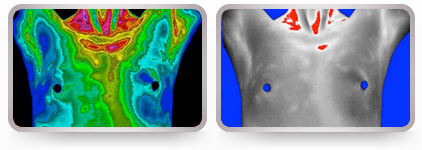
Minimal vascularity healthy breasts.
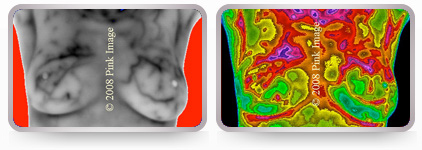
Vascular breasts that may be at risk.
HORMONE IMBALANCE
Hormonally balanced breast images that are non-vascular.
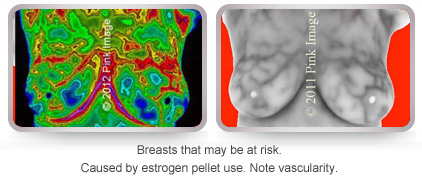
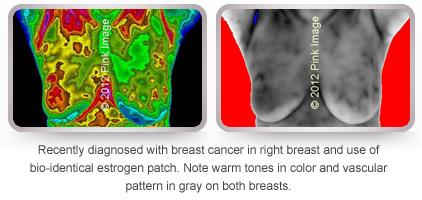
Bio-identical estrogen pellets, patches and creams may increase risk! Bio-identical estrogen stimulates breast cells and creates vascularity.
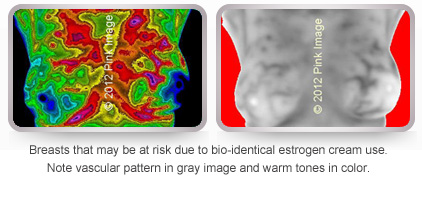
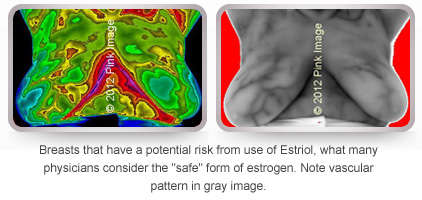
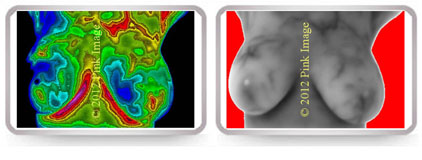
Soy contains phytoestrogens that may increase risk! Notice vascularity or activity of blood vessels caused by estrogen stimulation.
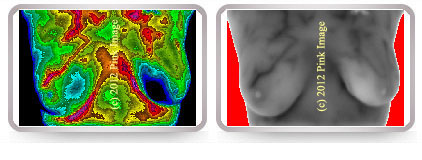
Another example of soy phytoestrogen stimulation of the breasts. Note vascularity.
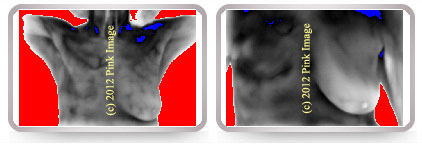
(left) Baseline scan of a patient with a diet high in soy and flax - note vascularity. (right) Patient removed these phytoestrogens from her diet. Note complete reduction in vascularity in left breast.
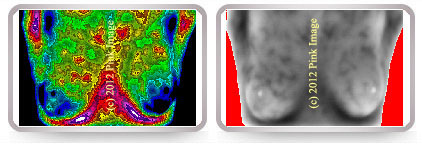
Patient utilizing Cohosh herbal therapy. Note vascularity.
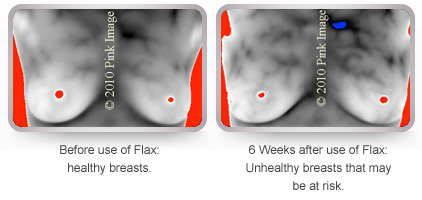
Flax contains phytoestrogens that may increase risk! Notice increase in vascularity or activity of blood vessels caused by estrogen stimulation.
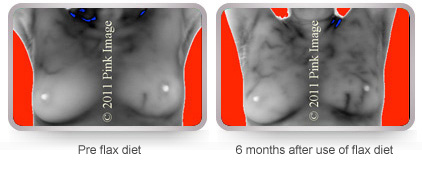
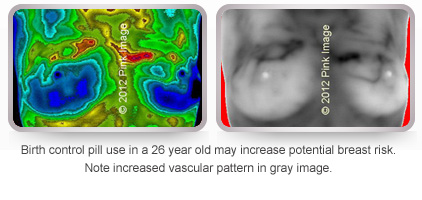
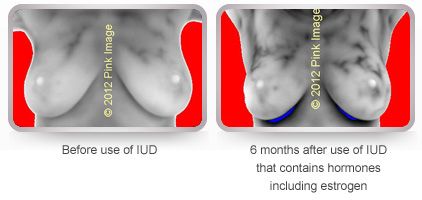
Synthetic estrogen contraceptives may increase risk! Synthetic estrogen stimulates breast cells and creates vascuarlity in the breasts causing a hormone imbalance.
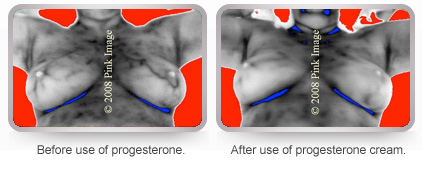
Progesterone cream (not pills) reduces estrogen stimulation and helps to create hormone balance. Must apply to breasts only! Notice reduction in vascularity. Patient reported decreased menopause symptoms!
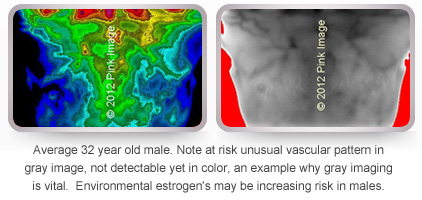
MALE BREAST CANCER
Male breast cancer is on the rise. In 2010 2,000 cases were reported with 400 deaths. Early detection with certified breast thermograhy is recommended.